Melasma Treatment Services by Dr. U in Los Angeles: Melasma (muh-LAZ-muh) is a skin problem that is very common. This condition results in brown to gray-brown patches on a person’s face; melasma on the face is the most commonly seen area of this condition. The majority of people get them on their cheeks, the bridge of their noses, on the forehead, chin, and right above their upper lip. However, it can also be present on other parts of the body that get a lot of sun exposure, like the forearms and neck. Melasma appears in more females than in males, making them more likely to receive treatment; only one in four to one in twenty individuals who are affected are men. This is in part due to the fact that melasma is more likely to appear during pregnancy, often referred to ask a “mask of pregnancy”. Melasma also generally shows on people with tan or dark skin more often than fairer skin types. Hormones might also play a role in triggering the on-sight of melasma.
This condition will likely start between the ages of twenty and forty years, but cases in children and beginning in middle age is not unheard of. Due to the wide variety of people experiencing this condition, many people of different genders and ages come to Dr. U seeking melasma treatment.
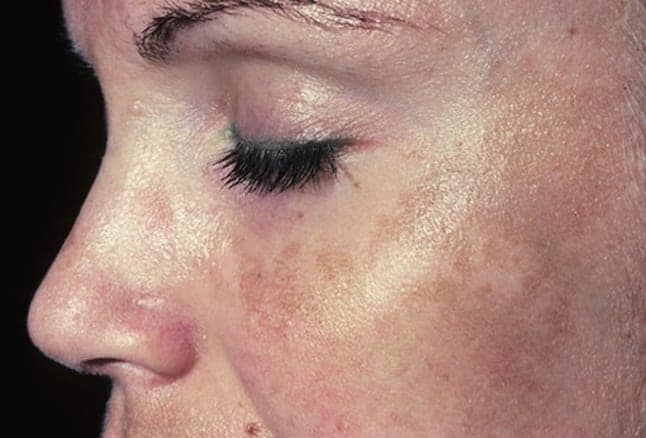
What Causes Melasma?
Melasma causes can be somewhat difficult to pinpoint. Most frequently, a genetic predisposition to melasma is the main reason for melasma development. This genetic component is present in a minimum of one in three patients claiming someone else in their family is affected as well. The majority of people will have melasma as a chronic disorder, causing them to seek out the best treatment options.
Melasma Triggers
- Sun damage and exposure— A risk factor that should strongly be avoided. For affected women who are pregnant, pigment usually diminishes a couple months after they have given birth.
- Hormone treatments— Oral birth control pills have estrogen and/or progesterone in them, replacement hormone, intrauterine devices as well as implants can factor in approximately one in four women who are affected.
- Certain kinds of medications (new targeted therapies for cancer), soaps that might be deodorant or scented, cosmetics and toiletries—these things can develop a phototoxic reaction that results in melasma, which then can continue long term.
- Hypothyroidism, as the thyroid hormones circulate at lower levels.
- Melasma usually appears in healthy, adults who aren’t pregnant. Experiencing sun exposure throughout your life can cause deposition of pigment within the dermis and this often happens for a long time. Melanin gets produced more because of ultraviolet radiation exposure (UVR) that deepen the pigmentation and activate the melanocytes. There is current research trying to narrow down the roles of vascular, neural, hormonal, and stem cell factors in contributing to the activation of the melanocyte.
How To Stop Melasma
The best way to avoid melasma is skin protection. If you want to avoid melasma treatment, then taking care of your skin while in the sun is crucial. Always apply broad-spectrum sunscreen, even if it isn’t sunny outside. Doing so can prevent an outbreak of melasma and may reduce the risk of current melasma getting worse. Apply sunscreen 20 minutes before you anticipate being outside. This a helpful measure to avoid melasma treatment down the line.
Types of Melasma
Epidermal
- Borders that are well-defined
- Darker brown color
- Easy to see under black light
- Does well with treatment
Dermal
- Not a very defined border
- Lighter bluish or brown in color
- Doesn’t change underneath a black light
- Doesn’t do very well with treatment
Mixed
- The most common kind
- Mixture of dark and light brown as well as bluish patches
- Combination of patterns seen under black light
- Responds somewhat with treatment
If you have a question about melasma treatment, do not hesitate to Ask Dr. U at no cost.
Melasma Treatment Options Using Topical Creams and Lotions
- Tyrosinase inhibitors are the mainstay of treatment. The goal of this treatment is to keep new pigment from forming by inhibiting formation of melanin by the melanocytes.
- Hydroquinone 2–4% as lotion or a cream, applied correctly to the pigmented areas during the evening for two to four months. This can result in contact dermatitis (redness and stinging) in a one fourth of the patients. It should not be used for long periods of time or in high concentration due to the fact that it has been linked with ochronosis (a grey and bluish discoloration identical to those seen in alkaptonuria).
- Azelaic acid cream, lotion or gel can be used twice daily long term, it’s also safe to apply during pregnancy. There may be a stinging sensation.
- Kojic acid dipalmitate or kojic acid dipalmitate is usually added with formulations, because it binds with copper, required by L-DOPA (a cofactor of tyrosinase). Kojic acid may cause allergic contact dermatitis as well as irritant contact dermatitis.
- Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) also acts within copper in order to inhibit pigment production. It is tolerated well but not very stable, that’s why typically other agents are combined with it.
- Methimazole (antithyroid drug) cream is said in hydroquinone-resistant melasma to be able to reduce pigmentation as well as melanin synthesis.
- New agents that are being investigated 4-hydroxy-anisole, deoxyarbutin and arbutin (from berries),5-dimethyl-4-hydroxy-3(2H)-furanone, zinc sulfate mequinol, rucinol, licorice extract, resveratrol, 2, and/or N-acetyl glucosamine.
There are some side effects to melasma treatments like temporary skin irritation. Those who have HQ treatment in very high concentrations for long periods of time (typically several months to years) can possibly develop a side effect called exogenous ochronosis. With this condition, the skin gets darker while the bleaching agent is used. Hydroquinone induced ochronosis is a permanent skin discoloration that is thought to be the result of the use of hydroquinone concentrations above 4%. There are reports of ochronosis responding to Alexandrite laser treatment.
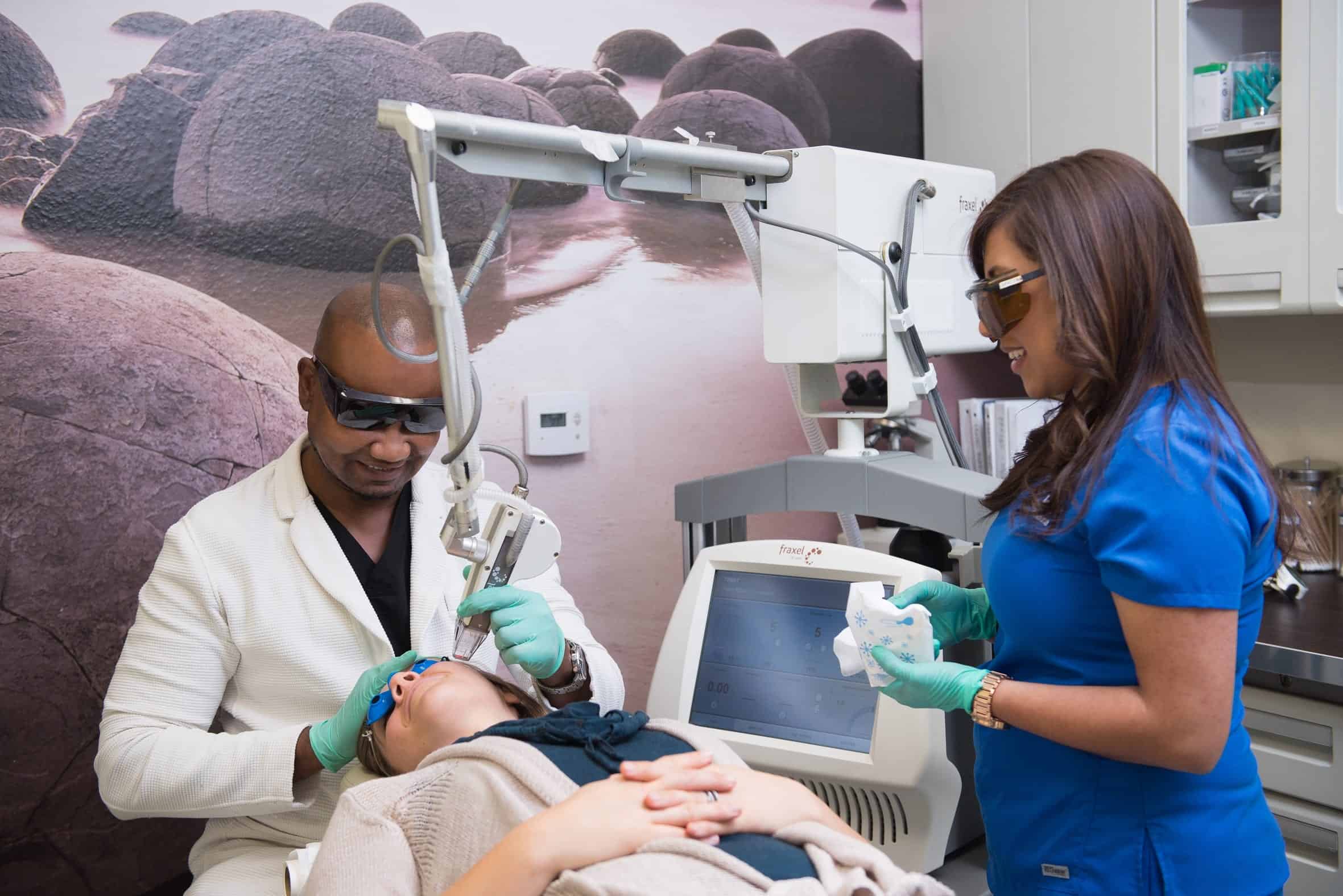
Dr. U Skin Clinic: Best Treatment of Melasma Using Lasers
The best melasma treatment will vary, depending on the patient. After a consultation, Dr. U will use the option most appropriate for the individual.
Nd: YAG Q-switch laser (1064 nm)
Works by destroying melanosomes to help treat signs of melasma and other hyper-pigmentation issues.
The melasma treatment with lasers works by irradiating the skin in a very exact manner to focus on and eliminate the organelles (within skin cells) containing the melanin, also known as melanosomes. Once these melanosomes have been eliminated, the body gets rid of the remains through a sloughing process. Usually for a brief period of time the skin becomes hypo-pigmented and looks lighter than normal. After that is done there is a repigmentation phase where the skin tone is restored.
Fraxel Dual Laser – FDA Approved for Melasma Treatment
In June 2013, the FDA approved the Fraxel Dual laser for the use of melasma treatment. Ethnic groups are safe to use this kind of energy wavelengths through the system. Fraxel Dual may also be used for other kinds of pigmentation issues like age spots which are also caused by the excess secretion of melanin that gets triggered by constant sun exposure.
Other lasers used for melasma treatment should be approached with caution. Ablative treatments like C02 lasers, erbium Yag and even IPL could paradoxically result in a worsening of melasma.
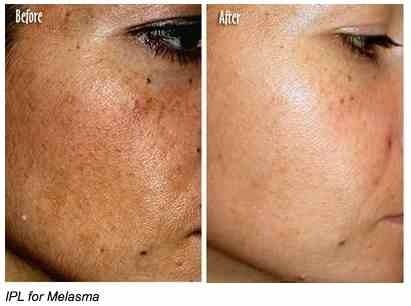
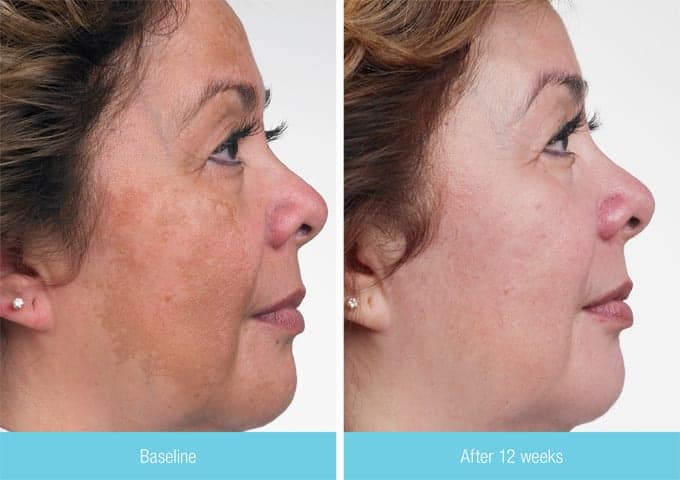
Before and After Melasma Treatment Services by Dr. U in Los Angeles
Facial Melanoma Treatment
Pigmentation Melasma Treatment
Melasma Treatment Services Los Angeles FAQ
How much does melasma treatment cost?
Cost for melasma treatment is individually based depending on the laser being used, the size of the melasma, and the amount of sessions needed. For an exact amount to match your needs reach out to Dr. U for a free online consultation.
How many melasma treatments will I need?
Typically, patients will need 3-4 treatments over a 3-6 month period.
Are there melasma natural treatment options available?
Some natural remedies have been proposed by some to improve melasma. However, these claims are not backed by strong scientific studies and they are not or approved by the FDA as melasma treatments. Some of these natural treatments include:
- Lemons
- Apple cider vinegar
- Turmeric
- Onion juice
- Aloe Vera
- Oatmeal
- Almonds
- Horseradish
- Papaya
- Sandalwood
Have more questions for Dr. U about melasma? Use the button below to send them:
Further Reading:
Find out more ways to remove age spots.
See how laser treatments can produce natural looking tattoo removal results.
